What is the Greenhouse Effect?
Please note that this material is from the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), published in 2007. The latest climate science can be found inthe IPCC’s 6th Assessment Report, published in August 2021. For other reports and further updates, please refer to theIPCC website.
This material is extracted from the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) section of the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), Working Group 1 (see full reference below).
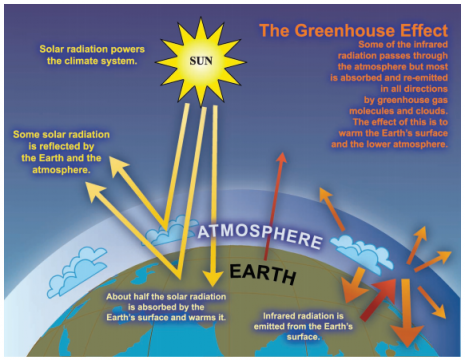
The Sun powers Earth’s climate, radiating energy at very short wavelengths, predominately in the visible or near-visible (e.g., ultraviolet) part of the spectrum. Roughly one-third of the solar energy that reaches the top of Earth’s atmosphere is reflected directly back to space. The remaining two-thirds is absorbed by the surface and, to a lesser extent, by the atmosphere. To balance the absorbed incoming energy, the Earth must, on average, radiate the same amount of energy back to space. Because the Earth is much colder than the Sun, it radiates at much longer wavelengths, primarily in the infrared part of the spectrum (see Figure 1). Much of this thermal radiation emitted by the land and ocean is absorbed by the atmosphere, including clouds, and reradiated back to Earth. This is called the greenhouse effect. The glass walls in a greenhouse reduce airflow and increase the temperature of the air inside. Analogously, but through a different physical process, the Earth’s greenhouse effect warms the surface of the planet. Without the natural greenhouse effect, the average temperature at Earth’s surface would be below the freezing point of water. Thus, Earth’s natural greenhouse effect makes life as we know it possible. However, human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels and clearing of forests, have greatly intensified the natural greenhouse effect, causing global warming.

FAQ 1.3, Figure 1. An idealised model of the natural greenhouse effect.
Reference
IPCC, 2007: Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment, Report of the Intergovernment Panel on Climate Change [Solomon, S., D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, M. Marquis, K.B. Averyt, M.Tignor and H.L. Miller (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA.
For a more detailed explanation of the answer please see the original IPCC FAQ document at:http://www.ipcc.ch/pdf/assessment-report/ar4/wg1/ar4-wg1-faqs.pdf
(0) Comments
There is no content