Water Sector Climate Change Adaptation Guidance Note

Introduction
Changes in mean climate conditions, climate variability, and climate extremes could impact the water sector in diverse ways in all continents. Across the African continent, climate change is expected to exacerbate existing water stress. Water scarcity is expected to be a major challenge for most of Asia due to increased water demand and poor water management. Across Europe, climate projections indicate a marked increase in heat waves, droughts, and heavy precipitation events. Lastly, significant trends in precipitation and temperature have been observed in Central America and South America, but the patterns vary regionally, with increasing trends in annual rainfall in southeastern South America and decreasing trends in Central America and central-southern Chile.
This water sector guidance note was prepared by the World Resources Institute (WRI) for the Islamic Development Bank (IsDB) to enable IsDB project teams to integrate information on climate risks into project design. It applies to water sector projects involving physical assets.
After a brief background on projected climate changes in regions and their projected impacts on the water sector (Section 2), Section 3 explains the purpose of this note within a broader climate risk management process. It describes the steps involved in managing a project’s climate change risks—beginning with climate risk screening, followed by project impact and adaptation assessments, and ending with project implementation. Section 4 then describes the process of determining potential climate impacts on water sector projects and identifying adaptation options to address those impacts. Section 5 presents an approach to evaluate adaptation options, and Section 6 concludes with two case studies(in Bangladesh and in Sierra Leone) that demonstrate how this approach may be applied in practice.
*Download the full guidance note from the right hand column. The key messages from the report are provided below. See the full text for much more detail. For your convenience, the guidance note is also available to read as an e-book via this link.
Supporting Climate Risk Management Process in the Water Sector
This guidance note will support the broader climate risk management process, which begins with climate risk screening and concludes with project implementation.
- The first phase of the process is climate risk screening.
- IsDB plans to begin using Acclimatise Aware, a climate risk screening tool, for this phase. In addition to generating an overall climate risk ranking, Aware identifies key climate risk areas for the project, based on project category and location.
- Project teams can use this information, along with expert judgment and other available climate data, to determine the climate hazards most likely to be relevant for a project. The World Bank’s Climate Change Knowledge Portal and The Nature Conservancy’s Climate Wizard are two examples of publicly available tools for identifying location-specific changes in climate conditions.
- If the initial climate risk screening using Aware indicates that a project has some level of climate risk, a project impact assessment follows. Climate risk screening and project impact assessment together establish the climate change vulnerability context of a project.
- That climate change vulnerability context informs the adaptation assessment that follows, which aims to identify those measures best suited to reduce climate vulnerability, thereby establishing a direct link between specific project activities and the overall objective of reducing climate vulnerability.
This guidance note is meant to support project impact and adaptation assessments of the climate risk management process.
Identifying Potential Impacts
The guidance, with decision trees, illustrates the process of identifying project vulnerabilities and adaptation options for projects involving:
- water resources extraction and conveyance structures;
- water and wastewater treatment facilities;
- treated water storage and distribution networks;
- sewerage and piped collection networks;
- and small-scale sanitation systems.
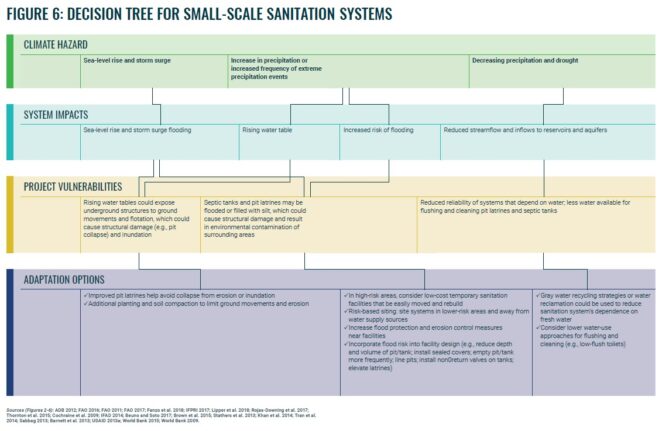
The guidance primarily focuses on the potential direct and indirect physical impacts of climate change. Physical impacts could also lead to any number of nonphysical impacts, but these tend to be highly context- and project-specific.
Upon identifying potential physical project vulnerabilities, project teams should consider whether such vulnerabilities could have follow-on consequences for a particular project.
Adaptation Options
Identifying Adaptation Options
Once a project team determines potential project vulnerabilities, it can proceed to identifying possible adaptation solutions.
An important preliminary step is defining the objective of adaptation. In setting objectives, project teams should consider:
- what vulnerabilities they seek to address
- what their desired outcomes are
Once the team defines its adaptation objectives, it should strive to compile a wide range of measures to meet those objectives.
Building resilience often requires a combination of hard and soft adaptation measures, as well as engineered and naturebased infrastructure options, because the underlying causes of vulnerability are often diverse.
- In identifying adaptation options, project teams should seek to develop a wide range of options.
Consulting with a variety of stakeholders (including community and nongovernmental organizations, environmental specialists, engineers, and others) can help to identify a comprehensive list of adaptation options.
- Finally, in identifying adaptation options, project teams should remember that adaptation measures will ideally be aligned with existing country or sector resilience plans.

Appraising Adaptation Options
For evaluating and prioritizing among adaptation options, the guidance describes an approach combining:
- Multi-criteria analysis:it allows for a qualitative and comparative assessment of different adaptation options. The project team would first identify the appropriate criteria for the given project, such as the following:
- Functional effectiveness
- Technical feasibility
- Affordability
- Stakeholder acceptability
- Ease of implementation
- Flexibility/robustness
- Cobenefits
- The remaining options can then be evaluated in greater detail using a quantitative economic assessment. Two possible techniques for economic assessment of adaptation options are:
- cost-benefit analysis
- cost-effectiveness analysis
- Rather than using economic assessments to identify the optimal solution for a single, best-guess projection, decision making under uncertainty is focused on increasing the robustness of a project. For example, by:
- Incorporating safety margins into adaptation planning
- Stress testing the outcomes of economic assessments using sensitivity analysis
- Identifying no-regret and low-regret measures to implement in the near term that will yield benefits regardless of the nature and extent of climate change
Case-studies
- Climate-Proofing Water Supply and Sanitation Infrastructure in Bangladesh
- Coupling Hard and Soft Adaptation Technologies for Sanitation in Sierra Leone
The guidance note was developed by the IsDB Climate Change Division (Dr. Ahmed Al Qabany, Olatunji Yusuf) under the general oversight of Dr. Mansur Muhtar, Vice President (Country Programs) and May Babiker, Acting Director, Resilience and Social Development Department. The guidance note was reviewed and received input from Dr. Nizar Zaied (Social Infrastructure Division, IsDB) and Nate Engle (World Bank). The main author of this guidance note was the World Resources Institute (WRI), technical consultant to the Islamic Development Bank.
This guidance note is part of a series developed by the IsDB Climate Change Division, which also includes:
- Agricultural and Rural Development Sectors Climate Change Adaptation Guidance Note
- Energy Sector Climate Change Adaptation Guidance Note
- Transport Sector Climate Change Adaptation Guidance Note
Suggested citation
World Resources Institute (2019) Water Sector Climate Change Adaptation Guidance Note. Islamic Development Bank: Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
(0) Comments
There is no content